| CAS
NO. |
546-88-3 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
208-913-8 |
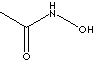
| FORMULA |
CH3CONHOH |
| MOL
WT. |
75.07 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
AHA; Lithostat;
Methylhydroxamic acid; N-Acetylhydroxylamine; |
| Acethydroxamsaeure;
Acetic acid, oxime; Acetohydroximic acid; Acetylhydroxamic acid;
Acide acetohydroxamique; Acido acetohidroxamico; Acidum acetohydroxamicum;
N-Acetylhydroxylamine; N-Hydroxyacetamide; |
| DERIVATION |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
CHELATING AGENTS / HYDROXAMIC ACIDS
/ |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to off-white crystalline
powder |
| MELTING POINT |
86
- 91 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
FLASH
POINT
|
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under normal conditions. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
Hydroxamic acid is an organic compound that contains the group -C(=O)NHOH; an
amine is is inserted into an carboxylic acid. This structure is useful for a
variety of roles in biology and medicine. This compound can be formed by
Angeli-Rimini reaction between an aldehyde and sulfinic acid or
N-hydroxysulfonamide. Hydroxamic acid structure provides a variety of roles in
biology and medicine (chelation therapy), It inhibits bacterial or fungi growth
by interfering with iron uptake. It is also active as a inhibitor of enzyme
involved in tumour growths. Marimastat is a hydroxamic acid active as an
Antineoplastic by inhibiting a matrix metalloproteinase. The most characteristic
property of hydroxamic acid is the metal binding (chelators). Sideromycins are
hydroxamic acid compounds active as antibiotic. Siderophores are hydroxamic acid
compounds produced by microorganisms for the abstraction of iron ions and
dissolve these ions as soluble Fe ion complexes for active transport mechanism.
Deferoxamine isolated from Streptomyces pilosus is a chelating agent used as an
antidote to iron poisoning. Hydroxamic acid compounds are used as extractants
for the separation of valuable metals or minerals including copper, lead, gold,
other rare earth metals and kaolin. Hydroxamic acids are used to produce
corresponding isocyanates by dehydration followed by rearrangement reaction. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white to off-white crystalline
powder |
|
ASSAY
|
98.0%
min
|
|
MELTING POINT |
86
- 91 C
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
1.0%
min
|
|
HEAVY
METALS
|
10ppm
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: T,
Risk
Phrases: 61, Safety Phrases: 53-45 |
